Mass Spectrometry Proteomics analysis discovers biomarkers in serum months to years before non-small cell lung cancer
The HUNT study
Olav Toai Duc Nguyen, Department of Clinical Research and Molecular Medicine, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim; Maria Markaki, Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics, University of Thrace, Alexandroupolis; Christina Chatzipantsiou, Department of Computer Science, University of Crete, Heraklion; Animesh Sharma, PROMEC, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim; Vincenzo Lagani, Institute of Chemical Biology, Ilia State University, Tibilisi; Ioannis Tsamardinos, JADBio Gnosis DA, Science and Technology Park of Crete, Department of Computer Science, University of Crete, Institute of Applied and Computational Mathematics, Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas; Oluf D. Røe, Department of Clinical Research and Molecular Medicine, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim
Digital Library: https://www.jto.org/article/S1556-0864(19)31769-1/fulltext
Abstract
The high incidence and high mortality rate of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) calls for identification of methods for early diagnosis. Early diagnosis is key for effective treatment and thereby increasing survival. Searching of cancer-related proteins and proteins signature in biofluids is an emerging approach in early diagnostic of malignancies. In the present study we have used proteomics-based profiling of serum collected 2 months to 5 years before NSCLC diagnosis to search for early diagnostic biomarkers.
Methods: All serum samples in this study were obtained from the Nord-Trøndelag Health Study (HUNT) Research Centre’s Biobank. Discovery sample set (Cohort I): Serum samples from 24 individuals that subsequently developed NSCLC (adenocarcinoma n=12, squamous cell carcinoma n=12) and 24 matched controls were obtained. Validation sample set (Cohort II): Serum samples from 10 future NSCLC patients (adenocarcinoma n=5, squamous cell carcinoma n=5) and 10 matched controls were obtained. The serum samples in both cohorts were collected in a time frame of 2 months to 5 years before diagnosis. All controls included were matched to the cases for smoking status (pack years and quit time), gender and age, and were cancer-free at least 5 years before blood sampling. All subjects were smokers or ex-smokers. Twenty (20) μl of serum was depleted of its high-abundant proteins and the cleaned-up peptides were analysed by LC- MS with an Orbitrap Elite mass spectrometer. Data were processed/analysed using MaxQuant software and JADBio AutoML.
Results
In the serum samples of Cohort I, a three-protein signature (AUC=0.692 [CI 0.515-0.748]) was detected where one protein was validated in Cohort II (Figure 2). The pathway analysis identified the pathways catecholamine biosynthesis (p=0.00278), phenylethylamine degradation I (p=0.00278) and LXR/RXR Activation (p=0.00312) as the top three most enriched pathways.
Conclusions: Proteomic analysis indicated that differential levels of a few proteins in serum may help detecting NSCLC 2 months to 5 years prior to clinical diagnosis. On the basis of the top differentially expressed proteins according to limma, IPA detected biologically relevant pathways. This is one of the first large-scale proteomics screening studies of pre-diagnostic serum of future NSCLC patients. Further validation studies are in progress.
How was JADBio used?
Reference and equivalent signatures were identified using JADBio with SES as feature selection algorithm. The JADBio matched pipeline with 50 repetitions for performance assessment (AUC with 95% CI) was used. On the basis of the top differentially expressed proteins by limma, pathway analysis was performed on Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software using p-value threshold of 0.05 and abs log2 fold change 0.5.
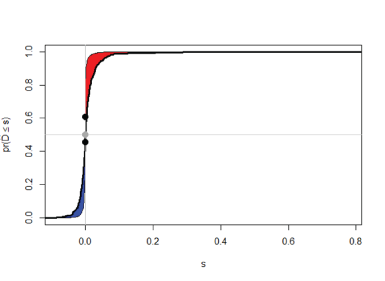
Figure 1. Supervised Principal Component Analysis based on the reference multivariable signature of SES (3 features/proteins) for the NSCLC contrast found using the JADBio with matching during cross-validation (red=cancer, blue= no cancer).
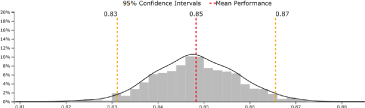
Figure 2. Beanplot of protein 1 upregulated in cases in Cohort I and validated in Cohort II.
Read more in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology
OTHER
Do you have questions?
JADBio can meet your needs. Ask one of our experts for an interactive demo.
Stay connected to get our news first!
Do you have questions?
JADBio can meet your needs. Ask one of our experts for an interactive demo.
Join the JADai Community!
Sign up with a FREE Basic plan! Be part of a growing community of AutoML enthusiasts
GET STARTED



